Kunshan Shuojing Photoelectric Technology Co., LTD
Mr. Jiang:18261685858
Mr. Jiang:13482461082
Email:gingerjzj@163.com
Adress:Room 809, Building 2, Jiayu International Business Plaza, Zhoushi Town, Kunshan City
Web address:shuojingcrystal.com
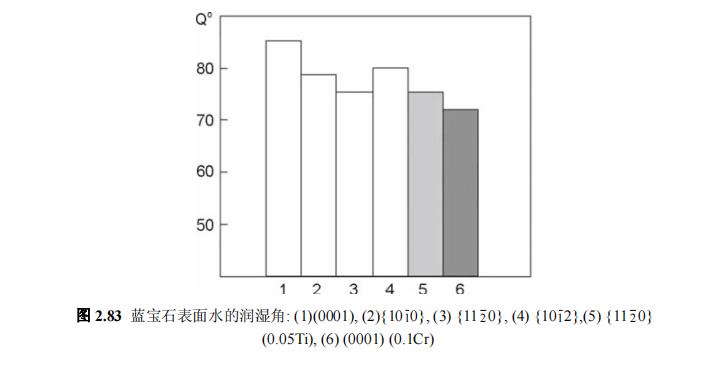
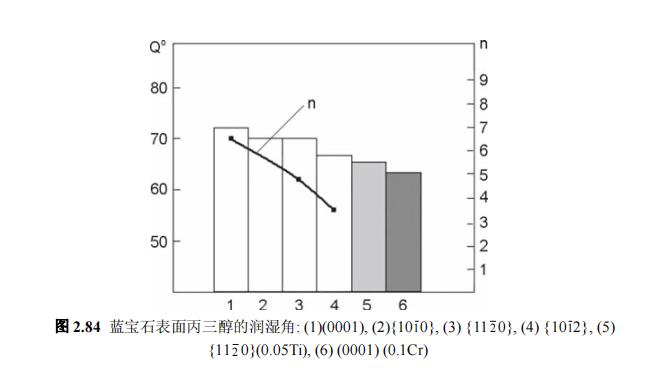
Wetability of sapphire crystals (2)
The wetting angles of sapphire major crystallographic planes in polar liquids (distilled water) and non-polar liquids (glycerol) are in the range of 68-85º (Figs. 2.83 and 2.84). Surface wetting on all samples studied The non-polar glycerol has a better wettability than water. The crystallographic orientation and dopant have a weak effect on the Q0 value, although the general characteristics of the change remain unchanged. Crystal doping is a Important factor. Doping with Cr (C=0.01%) leads to a decrease of 12º and 8º towards water and glycerol Q(0001)0, respectively. The same result is also found in Ti doping (C~0.05%), Q (11 2 0)0 decreased by 3º. In an isobaric solution of NaCl (0.9%), the crystal composition and crystallographic parameters were found to also have an effect on the wettability. This can be determined by the ionic composition of the solution (Na+ and Cl- ) on the investigated surface physicochemical adsorption process. The surface energy value of the sapphire crystallographic plane estimated from the wetting angle correlates with the wear resistance results of the previous tests. For {1010} and { The fastest wear rate of the 112 0} surface with free abrasives corresponds to the smallest Q0 value (maximum energy) (see Figure 2.83). This indicates that water is well involved in the wear process as a surface active species. The maximum biological inactivity corresponds to the smallest surface energy and the largest possible wetting angle, respectively. These data are also related to the corrosion resistance of different crystallographic planes of sapphire [100].
The physicochemical process in the treated area where water is present can be briefly described as follows. At the crystal-liquid interface, considerable adhesion forces occur between the liquid boundary layer molecules and the crystal surface. These forces hinder sliding on the interface. Wetting The phenomenon is usually explained by the interaction of such positions. Surfaces in friction are generally separated by a thin lubricating layer that is so tightly bound that direct contact of these surfaces is ruled out, and relative dislocations occur along an intermediate liquid layer . The surface activity of a liquid is determined by its molecular structure. The higher the molecular polarity, the stronger the activity. When the liquid molecules adsorbed on the crystal surface can move, the molecular interactions are conducted along the micro-cracks in the crystal of the adjacent layer on the surface. Liquid molecules The wedging effect (Rebinder effect) makes the micro-cracks develop into macro-cracks, and thus causes the particles to be exfoliated from the crystal surface, thus facilitating the diffusion process. Because water wets the {1010} and {112 0} planes during the friction process Better, so that the maximum wear rate can be observed on these faces.
Therefore, the dependence of the wetting of sapphire with water and glycerol and the crystallographic direction is studied. The maximum wetting angle with these two liquids is on the (0001) plane. The minimum wetting angle for water is at {1010} and {112 0} planes and {1012} planes for glycerol. The water wettability of the major crystallographic planes of sapphire is related to the wear rate of these planes under friction with free abrasives in water as a suspension medium A correlation was found between them.
Kunshan Shuojing Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. is involved in a wide range of new materials, and has complete preparation methods and means for functional ceramics and sapphire crystals, scintillation crystals, and laser crystals, forming optically transparent ceramics, sapphire optical windows, scintillation crystals, lasers and nonlinear crystals The main four series of high-tech products.